
 10001629119
10001629119
Price Listing
RM 1460 AM Session
Excluding 8% SST
Terms & ConditionsAsk a consultant
Have questions?
Our dedicated team of specialists are here to help you!
Get in touch and speak to our friendly team:
Our Team |
[email protected] | +603-6204 8941
or find us on:
Normal Price
Online
RM 1460 AM Session
Excluding 8% SST
Ask a consultant
Have questions?
Our dedicated team of specialists are here to help you!
Get in touch and speak to our friendly team:
Our Team |
[email protected] | +603-6204 8941
or find us on:
Normal Price
Online
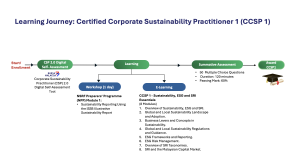 Participants may proceed to enrol for CCSP 1 by registering for the following components:
Participants may proceed to enrol for CCSP 1 by registering for the following components:
- Workshop: NSRF Preparers’ Programme (NPP) Module 1 – Sustainability Reporting Using the ISSB Illustrative Sustainability Report; and
- E-learning and Assessment
| Workshop: NSRF Preparers’ Programme (NPP) Module 1: Sustainability Reporting Using the ISSB Illustrative Sustainability Report (1-day physical workshop) | ||
| Workshop Date | Fee (RM) excl. SST | Registration Link |
| 5 Feb 2026 | 1,288 | Register |
| 13 May 2026 | 1,288 | Register |
| 8 July 2026 | 1,288 | Register |
| 2 Sep 2026 | 1,288 | Register |
| 17 Nov 2026 | 1,288 | Register |
| E-learning and Assessment: (3 months access to the E-learning before the Assessment date) Important Note: Participants must attend the Workshop: NSRF Preparers’ Programme (NPP) Module 1 before registering for the E-learning and Assessment component. | ||
| Assessment Date | Fee (RM) excl. SST | Registration Link |
| 29 Jan 2026 | 1,460 | Register |
| 30 Mar 2026 | 1,460 | Register |
Programme Objective
Learning Outcome
- explain key sustainability factors, concepts, principles, strategies, and methodologies used to evaluate and strengthen a corporate sustainability framework.
- interpret and apply key concepts and requirements of the sustainability reporting landscape, including the assurance ecosystem, conceptual foundations, and mandatory disclosure requirements.
- integrate ESG principles, strategies, and methodologies into organisational decision-making, operations, and governance processes in accordance with Malaysian regulatory requirements, established taxonomies, standards, and best practices.
- conduct sustainability assessments using recognised methodologies, relevant data, and criteria to evaluate compliance and alignment with Malaysian regulatory frameworks, taxonomies, standards, and best practices, and to provide informed recommendations for organisational sustainability initiative
- Methodology
- Competencies
- Entry Requirements
- Duration of Modules
- Target Audience
- Completion Requirements
Methodology
Certified Corporate Sustainability Practitioner 1 (CCSP1) is conducted via blended mode and comprises the following components:
- Bursa Malaysia Corporate Sustainability Practitioner (CSP) 2.0 Digital Self-Assessment Tool;
- Workshop: NSRF Preparers’ Programme (NPP) Module 1 – Sustainability Reporting Using the ISSB Illustrative Sustainability Report,
- eLearning: CCSP 1 – Sustainability, ESG and SRI Essentials; and
- CCSP 1 Summative Assessment
- CC03 Corporate Governance
- FOR04 Capital Market Products Regulations
- FOP05 Sustainable and Responsible Investment Products
- FUT10 Sustainability/SRI Analysis
Entry Requirements
- Possess a degree or professional qualification from recognised institution; or
- Possess a diploma from a recognised institution with a minimum 2 years of working experience
Duration of Modules
- Bursa Malaysia Corporate Sustainability Practitioner (CSP) 2.0 Digital Self-Assessment Tool.
- Workshop = 1-day workshop.
- e-Learning Modules (8 Modules) = 30 minutes per module.
- Summative Assessment = 120 minutes
Target Audience
Completion Requirements
- Completion of the Bursa Malaysia Corporate Sustainability Practitioner (CSP) 2.0 Digital Self-Assessment Tool
- Completion of Workshop: NSRF Preparers’ Programme (NPP) Module 1 – Sustainability Reporting Using the ISSB Illustrative Sustainability Report,
- Completion of e-Learning: CCSP 1 – Sustainability, ESG and SRI Essentials or Sustainability, ESG and SRI Essentials; and
- Passing CCSP 1 Summative assessments.
